introduction
a. definition
A surgery to remove fluid and cut off part of the tunica vaginalis testis
b. scope
All patients who present with scrotal swelling and on examination found a positive transillumination test.
Hydrocele is fluid buildup between the tunica vaginalis testis.
In regard to diagnosis and treatment, required related disciplines of Radiology.
c. indications of surgery
Hydrocele:
- Large that it can suppress the blood vessels to the testicles
- Interfere with or disrupt the activities of daily
- Disturbing cosmetic
d. Contra indications of operation:
general
e. Diagnoses
- Testicular Tumors
- Epididymal Cyst
- Spermatocele
- Hernia scrotalis
f. examination Support
Ultrasound examination when clinical doubt.
Technical Operations
Briefly the technique of hidrokelektomi can be explained as follows:
· With regional or general anesthesia.
· Position the patient supine (supine).
· Disinfection of surgical field with an antiseptic solution.
· Field surgically narrowed with sterile linen.
· Skin incision in the scrotum raphe on the most prominent layer by layer until it looks the tunica vaginalis.
· Guide to meluksir hydrocele blunt preparation, if done immense aspirations hidrokelnya contents of the bag first.
· Incisions are the most prominent part of the hydrocele, then do:
o Techniques Jaboulay: dimarsupialisasi parietal tunica vaginalis and when necessary diplikasi with chromic cat gut string.
Technique o Lord: the tunica vaginalis parietalis diplikasi excised and the edges with yarn chromic cat gut.
· Operation wound was closed layer by layer with threads chromic cat gut.
complications of surgery
Post-surgical complication is bleeding and surgical wound infections.
mortality
(none)
Post-Surgical Care
Treat the wound day 3.
Friday, August 26, 2011
Modified radical mastectomy (MRM)
Introductions:
a. Definition
Modified Radical Mastectomy is a surgical oncologist action on breast malignancy is to remove the entire breast tissue consisting of stroma and parenkhim entire breast, areola and nipple and the skin over the tumor with axillary lymph node dissection ipsilateral level I, II / III en bloc WITHOUT lifting m.pektoralis major and minor.
b. Scope
The breast is the breast stroma and parenkhim located in the anterior wall of the piston between the ICS II and VI and parasternal up to the line axilaris medius. Breast primary vascularization of the branch gets a. the internal mammary, a. Torakoakromialis and branch a. Intercostal 3,4,5.
Regional lymph nodes in the breast is axillary lymph nodes, supra-and infraclavicular and internal mammary. Axillary nodes are divided into three zones namely Level I, II and III. Level I is the KGB is located lateral to the pectoralis minor muscular, level II is located behind the KGB m.pektoralis minor and Level III is located medially of the KGB m.pektoralis minor. Besides, there is also a KGB interpektoral or called Rotter.
Tumors of the breast is divided into
· Benign tumors: fibroadenomas, cysts,
· Malignant tumors: invasive ductal, invasive lobular and other variants (mucoid, papillary, medullary, kribriform etc.)
· Situ malignancy: lobular in situ, in situ ductal and mikroinvasif
Until now the exact cause of breast cancer, is unknown because it is multifactorial
Breast cancer risk factors:
Age of> 35 years
· Menarche <12 years
· Menopause> 55 years
· Nullipara
· Family history (parents, siblings) with breast cancer
Breast cancer diagnosis is made by:
· Diagnosis confirmation of malignancy: clinical examination, FNA & imaging (mammography and / or breast ultrasound. (Tripple diagnostic)
· Diagnosis stage breast cancer: clinical examination, laboratory and imaging (ultrasound images toraks/paru- liver/abdomen- k / p bone scanning).
In circumstances where one component of the triple diagnostic discrepancy experienced biopsy interpretation is done by examination of frozen pieces (if there are facilities) or biopsy only had to know what type of histopatologinya. Subsequent therapy depends on the outcome histopatologinya
c. Indications of surgery
· Cancer early-stage breast (I, II)
· Cancer locally advanced breast with specific requirements
· Soft tissue malignancies of the breast.
d. Contra indications operation
· Tumor attached to the chest wall
· Edema of the arm
· Extensive satellite nodules
· Mastitis inflamatoar
e. Differential diagnosis
· Other malignancies of the breast (sarcoma, lymphoma, etc.).
· Phylodes tumors (malignant and benign).
· Mastitis spacious (especially tuberculous mastitis)
f. Investigations
· Mandatory
- Mammography and / or breast ultrasound
- CXR
- FNAB of breast tumors
- Ultrasound liver / abdomen
- Complete blood chemistry examination in preparation for surgery
· Oprional
- Bone scanning
- Chemical examination of blood / tumor markers: CEA, Ca 15-3, CA 125
Engineering operations
In brief, the operating technique of modified radical mastectomy can be explained as follows:
1. Patients in general anesthesia, the arm ipsilateral to the operated positioned abduction 900, ipsilateral to the operated shoulder propped a thin pillow.
2. Disinfection of the operating field, the upper and mid-neck, the bottom up to the umbilicus, medial to the mid mammma contralateral, lateral to the lateral edge of the scapula. Disinfected circular upper arm until the elbow is then wrapped with sterile doek followed by narrowing the operating field with sterile doek
3. When you get ulcers on the breast tumor, the ulcer should be covered with sterile gauze thick (Buick Gaas) and circular stitches.
4. Do incision (various incision is Stewart, Orr, Willy Meyer, Halsted, incision S) where the line of incision is at least within 2 cm from the edge of the tumor, then created a flap.
5. Flap top to below the clavicle, medially to parasternal ipsilateral flap, flap down to the inframammary fold, the flap lateral to the anterior edge of the m. Latissimus dorsi and identify vasa and. N. Thoracalis dorsalis
6. Mastectomy started from the medial to lateral while caring for bleeding, especially branches of the intercostal blood vessels in the parasternal area. At the time until the lateral edge of the mayor with the help of Haak m.pektoralis maamma tissue removed from the m. Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior (simple mastectomy). In a radical mastectomy pectoralis muscle has begun to
7. Axillary dissection begins with finding the existence of Level I axillary lymph nodes enlargement (lateral pectoralis minor), level II (behind the pectoralis minor) and level III (medial pectoralis minor). Dissection is not higher in vasa axillary region, because it can lead to arm edema. Veins leading to the network mamma ligated. Further identify vasa and n. Thoracalis longus, and thoracalis dorsal, interkostobrachialis. Internerural KGB and eventually further didiseksi mamma tissue and axillary lymph nodes as a single unit detached (en bloc)
8. Field operations sublimat and washed with a solution of 0.9% Nacl.
9. All the tools used during surgery was replaced with a new set, as well as handschoen operators, assistants and instruments as well as doek sterility.
10. Re-evaluation of the source of bleeding
11. 2 pieces mounted drain, a large drain (Redon no. 14) is placed under the vasa axillary, being a smaller drain (12) is directed medially.
12. Surgical wound was closed lapais by layer
Complications of surgery
Early: - bleeding,
- Lesions n. Thoracalis longus à wing scapula
- Lesions n. Thoracalis dorsalis.
Slow: - infection
- Necrosis of flap
- Wound dehiscence
- Seroma
- Edema of the arm
- Stiffness of the shoulder joint contractures à
Mortality
almost no
Post-surgical care
Post-surgical patients admitted to the room by observing the drain production, post-surgical check Hb. Rehabilitation as soon as possible by exercising the shoulder joint movement. Drain removed when the production of each drain <20 cc/24 hours. Generally medial removable drain early, because fewer production. Stitches are generally removed the day ke10 s / d 14.
Follow-up
Year 1 and 2 à controls every 2 months
Year 3 s / d 5 à controls every 3 months
After year 5 à controls every 6 months
Physical examination: each time the control
Thorax picture: every 6 months
Lab. Marker: every 2-3 months
Contralateral mammography: every year or there are indications
Abdominal ultrasound: every 6 months or no indication
Bone scanning: every 2 years or no indication
a. Definition
Modified Radical Mastectomy is a surgical oncologist action on breast malignancy is to remove the entire breast tissue consisting of stroma and parenkhim entire breast, areola and nipple and the skin over the tumor with axillary lymph node dissection ipsilateral level I, II / III en bloc WITHOUT lifting m.pektoralis major and minor.
b. Scope
The breast is the breast stroma and parenkhim located in the anterior wall of the piston between the ICS II and VI and parasternal up to the line axilaris medius. Breast primary vascularization of the branch gets a. the internal mammary, a. Torakoakromialis and branch a. Intercostal 3,4,5.
Regional lymph nodes in the breast is axillary lymph nodes, supra-and infraclavicular and internal mammary. Axillary nodes are divided into three zones namely Level I, II and III. Level I is the KGB is located lateral to the pectoralis minor muscular, level II is located behind the KGB m.pektoralis minor and Level III is located medially of the KGB m.pektoralis minor. Besides, there is also a KGB interpektoral or called Rotter.
Tumors of the breast is divided into
· Benign tumors: fibroadenomas, cysts,
· Malignant tumors: invasive ductal, invasive lobular and other variants (mucoid, papillary, medullary, kribriform etc.)
· Situ malignancy: lobular in situ, in situ ductal and mikroinvasif
Until now the exact cause of breast cancer, is unknown because it is multifactorial
Breast cancer risk factors:
Age of> 35 years
· Menarche <12 years
· Menopause> 55 years
· Nullipara
· Family history (parents, siblings) with breast cancer
Breast cancer diagnosis is made by:
· Diagnosis confirmation of malignancy: clinical examination, FNA & imaging (mammography and / or breast ultrasound. (Tripple diagnostic)
· Diagnosis stage breast cancer: clinical examination, laboratory and imaging (ultrasound images toraks/paru- liver/abdomen- k / p bone scanning).
In circumstances where one component of the triple diagnostic discrepancy experienced biopsy interpretation is done by examination of frozen pieces (if there are facilities) or biopsy only had to know what type of histopatologinya. Subsequent therapy depends on the outcome histopatologinya
c. Indications of surgery
· Cancer early-stage breast (I, II)
· Cancer locally advanced breast with specific requirements
· Soft tissue malignancies of the breast.
d. Contra indications operation
· Tumor attached to the chest wall
· Edema of the arm
· Extensive satellite nodules
· Mastitis inflamatoar
e. Differential diagnosis
· Other malignancies of the breast (sarcoma, lymphoma, etc.).
· Phylodes tumors (malignant and benign).
· Mastitis spacious (especially tuberculous mastitis)
f. Investigations
· Mandatory
- Mammography and / or breast ultrasound
- CXR
- FNAB of breast tumors
- Ultrasound liver / abdomen
- Complete blood chemistry examination in preparation for surgery
· Oprional
- Bone scanning
- Chemical examination of blood / tumor markers: CEA, Ca 15-3, CA 125
Engineering operations
In brief, the operating technique of modified radical mastectomy can be explained as follows:
1. Patients in general anesthesia, the arm ipsilateral to the operated positioned abduction 900, ipsilateral to the operated shoulder propped a thin pillow.
2. Disinfection of the operating field, the upper and mid-neck, the bottom up to the umbilicus, medial to the mid mammma contralateral, lateral to the lateral edge of the scapula. Disinfected circular upper arm until the elbow is then wrapped with sterile doek followed by narrowing the operating field with sterile doek
3. When you get ulcers on the breast tumor, the ulcer should be covered with sterile gauze thick (Buick Gaas) and circular stitches.
4. Do incision (various incision is Stewart, Orr, Willy Meyer, Halsted, incision S) where the line of incision is at least within 2 cm from the edge of the tumor, then created a flap.
5. Flap top to below the clavicle, medially to parasternal ipsilateral flap, flap down to the inframammary fold, the flap lateral to the anterior edge of the m. Latissimus dorsi and identify vasa and. N. Thoracalis dorsalis
6. Mastectomy started from the medial to lateral while caring for bleeding, especially branches of the intercostal blood vessels in the parasternal area. At the time until the lateral edge of the mayor with the help of Haak m.pektoralis maamma tissue removed from the m. Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior (simple mastectomy). In a radical mastectomy pectoralis muscle has begun to
7. Axillary dissection begins with finding the existence of Level I axillary lymph nodes enlargement (lateral pectoralis minor), level II (behind the pectoralis minor) and level III (medial pectoralis minor). Dissection is not higher in vasa axillary region, because it can lead to arm edema. Veins leading to the network mamma ligated. Further identify vasa and n. Thoracalis longus, and thoracalis dorsal, interkostobrachialis. Internerural KGB and eventually further didiseksi mamma tissue and axillary lymph nodes as a single unit detached (en bloc)
8. Field operations sublimat and washed with a solution of 0.9% Nacl.
9. All the tools used during surgery was replaced with a new set, as well as handschoen operators, assistants and instruments as well as doek sterility.
10. Re-evaluation of the source of bleeding
11. 2 pieces mounted drain, a large drain (Redon no. 14) is placed under the vasa axillary, being a smaller drain (12) is directed medially.
12. Surgical wound was closed lapais by layer
Complications of surgery
Early: - bleeding,
- Lesions n. Thoracalis longus à wing scapula
- Lesions n. Thoracalis dorsalis.
Slow: - infection
- Necrosis of flap
- Wound dehiscence
- Seroma
- Edema of the arm
- Stiffness of the shoulder joint contractures à
Mortality
almost no
Post-surgical care
Post-surgical patients admitted to the room by observing the drain production, post-surgical check Hb. Rehabilitation as soon as possible by exercising the shoulder joint movement. Drain removed when the production of each drain <20 cc/24 hours. Generally medial removable drain early, because fewer production. Stitches are generally removed the day ke10 s / d 14.
Follow-up
Year 1 and 2 à controls every 2 months
Year 3 s / d 5 à controls every 3 months
After year 5 à controls every 6 months
Physical examination: each time the control
Thorax picture: every 6 months
Lab. Marker: every 2-3 months
Contralateral mammography: every year or there are indications
Abdominal ultrasound: every 6 months or no indication
Bone scanning: every 2 years or no indication
Water Pipe Fitting Seal Intratorakal or Drainage
Introductiona. Definition
Invasive action by inserting a hose or tube into the thoracic cavity by penetrating the muscular intercostalisb. Scope
Distribute both substances in the form of solids, liquids, air or gas from the chest cavityc. Operation Indication
- More than 30% pneumothorax.
- Pneumothorax residif
- Bilateral pneumothorax
- Hematothoraks more than 300cc
- Hematothoraks bilateral
- Hemato-pneumothorax
- Flail-chest
- Fluidothoraks is superb, with shortness of
- Chylothoraks
- Empyema thoracis after dipungsi unsuccessful or pus is very thick
- Post thoracotomid. Contra Indications:
- General
- Special (no)e. Diagnoses
Nof. Examination Support
- CXRTechnical operations
Installation WSD
1. Patients in a state of half sitting position (+ 45 °).
2. Carried out disinfection and closing with doek sterile operating field.
3. Do local anesthesia with 2% lidocain in infiltration in the area of skin to the pleura.
4. Places that will be installed drain is:
- Linea front axillary line, the ICS IX-X (Buelau).
Can be more proximal, if necessary. Especially in children because the location of the diaphragm
high.
- Linea medio-clavicularis (MCL) in the ICS II-III (Monaldi)
5. Created 2 cm long skin incision until the tissue under the skin.
6. Listed vertical mattress sutures anchoring is tilted to the side 0.1.
7. With tipped curved scissors or blunt clamp curved, subcutaneous tissue freed up the pleura, the pleural penetrated slowly until you hear a sucking sound, it means that the parietal pleura was opened.
Note: on hematothoraks will soon be spraying blood out, the pneumothorax, the air comes out.
1. Drain the trocarnya inserted through the hole towards the cranial lateral skin. When using the drain without trocar, then the end of the drain is clamped with a blunt clamp, to facilitate direct drain.
2. Should be checked first, if the drain is made or there are enough holes side length approximately the distance from apex to the aperture of the skin, duapertinganya.
3. Drain then pushed while playing a little lateral direction until the tip is below about lung apex (Bulleau).
4. After the drain in position, then tied with string fastener rotating double, ending with a slip knot
5. When used according to Monaldi drainage, the drain is driven downwards and laterally until the tip approximately mid-thoracic ronga.
6. Before the drainage pipe system connected to the reservoir bottle, it must be clamped first.
7. Drainage pipe is then connected to the reservoir bottle system, which will guarantee the re-occurrence of negative pressure in the intrapleural cavity, in addition will also accommodate sekrit out of the thoracic cavity.Complication
When done correctly, complications can be avoided. But it can also occur kutis emphysema, False route on the liver when installed too low on the right, especially in children because the location of the diaphragm is still highMortality
Very low morbidity, mortality 0%Post-Installation Care WSD
1. The patient is placed on a semi-sitting position (+ 30 °)
2. The entire drainage system: pipes, bottles, should be in neat, there are no riots arrangement, and can be immediately seen.
3. pipe that comes out of the thoracic cavity must be fixed to the body with plaster wide, orange to prevent wobble.
4. By using a transparent pipe, it can be seen the release of secretions. Must be maintained that the secretions out smoothly. When visible blood clots or other, must be milked until smooth again.
5. Every day should be the control piston AP photo to see:
- Lung condition
- The position of drain
- Other abnormalities (emphyema, shadow mediastonim)
1. The number on the bottle sekrit shelters should be calculated:
- Many sekrit out (every hour - every day)
- Kinds sekrit out (pus, blood, etc.)
7. In patients with respiratory physiotherapy has always done
8. Any abnormalities in the drain should be immediately corrected.Post-Installation Care WSD
1. The patient is placed on a semi-sitting position (+ 30 °)
2. The entire drainage system: pipes, bottles, should be in neat, there are no riots arrangement, and can be immediately seen.
3. pipe that comes out of the thoracic cavity must be fixed to the body with plaster wide, orange to prevent wobble.
4. By using a transparent pipe, it can be seen the release of secretions. Must be maintained that the secretions out smoothly. When visible blood clots or other, must be milked until smooth again.
5. Every day should be the control piston AP photo to see:
- Lung condition
- The position of drain
- Other abnormalities (emphyema, shadow mediastonim)
1. The number on the bottle sekrit shelters should be calculated:
- Many sekrit out (every hour - every day)
- Kinds sekrit out (pus, blood, etc.)
1. In patients with respiratory physiotherapy has always done
2. Any abnormalities in the drain should be immediately corrected.
Revocation guidelines
1. Criteria for revocation
- Sekrit serous, not hemorage
Adults: the amount is less than 100cc/24jam
Children - children: less number 25-50cc/24jam
- Lung expands
Clinical; sound right = left lung expands
Evaluation of chest X-ray
1. Condition:
- In the trauma
Hemato / pneumothorak who already meet both criteria, immediately revoked by the water-tight (air tight).
- In thoracotomi
a. Infection: 24h clamps to prevent resufflasi first, if either unplug.
b. Post operative: if it fulfills both criteria, langsug revoked (water-tight)
c. Post pneumonectomy: day-to-3 when the mediastinum is stable (does not need water-tight
1. Alternative
1. Permanent lung collapse, suction up to 25 cmH20:
- If both krieria met, the clamps first 24 hours, fixed baikà unplug.
- If unsuccessful, wait until 2minggu à dekortikasi
1.
1. Sekrit over 200cc/24jam: suspicion of thoracic Chylo (make sure the laboratory), keep up with 4minggu.
- If unsuccessful à Toracotomi
- If less than 100cc/24jam sekrit, clamps, and then revoked.Follow - Up
Aimed at the onset of further complications such as empyema, Schwarte, impaired respiratory function.
Invasive action by inserting a hose or tube into the thoracic cavity by penetrating the muscular intercostalisb. Scope
Distribute both substances in the form of solids, liquids, air or gas from the chest cavityc. Operation Indication
- More than 30% pneumothorax.
- Pneumothorax residif
- Bilateral pneumothorax
- Hematothoraks more than 300cc
- Hematothoraks bilateral
- Hemato-pneumothorax
- Flail-chest
- Fluidothoraks is superb, with shortness of
- Chylothoraks
- Empyema thoracis after dipungsi unsuccessful or pus is very thick
- Post thoracotomid. Contra Indications:
- General
- Special (no)e. Diagnoses
Nof. Examination Support
- CXRTechnical operations
Installation WSD
1. Patients in a state of half sitting position (+ 45 °).
2. Carried out disinfection and closing with doek sterile operating field.
3. Do local anesthesia with 2% lidocain in infiltration in the area of skin to the pleura.
4. Places that will be installed drain is:
- Linea front axillary line, the ICS IX-X (Buelau).
Can be more proximal, if necessary. Especially in children because the location of the diaphragm
high.
- Linea medio-clavicularis (MCL) in the ICS II-III (Monaldi)
5. Created 2 cm long skin incision until the tissue under the skin.
6. Listed vertical mattress sutures anchoring is tilted to the side 0.1.
7. With tipped curved scissors or blunt clamp curved, subcutaneous tissue freed up the pleura, the pleural penetrated slowly until you hear a sucking sound, it means that the parietal pleura was opened.
Note: on hematothoraks will soon be spraying blood out, the pneumothorax, the air comes out.
1. Drain the trocarnya inserted through the hole towards the cranial lateral skin. When using the drain without trocar, then the end of the drain is clamped with a blunt clamp, to facilitate direct drain.
2. Should be checked first, if the drain is made or there are enough holes side length approximately the distance from apex to the aperture of the skin, duapertinganya.
3. Drain then pushed while playing a little lateral direction until the tip is below about lung apex (Bulleau).
4. After the drain in position, then tied with string fastener rotating double, ending with a slip knot
5. When used according to Monaldi drainage, the drain is driven downwards and laterally until the tip approximately mid-thoracic ronga.
6. Before the drainage pipe system connected to the reservoir bottle, it must be clamped first.
7. Drainage pipe is then connected to the reservoir bottle system, which will guarantee the re-occurrence of negative pressure in the intrapleural cavity, in addition will also accommodate sekrit out of the thoracic cavity.Complication
When done correctly, complications can be avoided. But it can also occur kutis emphysema, False route on the liver when installed too low on the right, especially in children because the location of the diaphragm is still highMortality
Very low morbidity, mortality 0%Post-Installation Care WSD
1. The patient is placed on a semi-sitting position (+ 30 °)
2. The entire drainage system: pipes, bottles, should be in neat, there are no riots arrangement, and can be immediately seen.
3. pipe that comes out of the thoracic cavity must be fixed to the body with plaster wide, orange to prevent wobble.
4. By using a transparent pipe, it can be seen the release of secretions. Must be maintained that the secretions out smoothly. When visible blood clots or other, must be milked until smooth again.
5. Every day should be the control piston AP photo to see:
- Lung condition
- The position of drain
- Other abnormalities (emphyema, shadow mediastonim)
1. The number on the bottle sekrit shelters should be calculated:
- Many sekrit out (every hour - every day)
- Kinds sekrit out (pus, blood, etc.)
7. In patients with respiratory physiotherapy has always done
8. Any abnormalities in the drain should be immediately corrected.Post-Installation Care WSD
1. The patient is placed on a semi-sitting position (+ 30 °)
2. The entire drainage system: pipes, bottles, should be in neat, there are no riots arrangement, and can be immediately seen.
3. pipe that comes out of the thoracic cavity must be fixed to the body with plaster wide, orange to prevent wobble.
4. By using a transparent pipe, it can be seen the release of secretions. Must be maintained that the secretions out smoothly. When visible blood clots or other, must be milked until smooth again.
5. Every day should be the control piston AP photo to see:
- Lung condition
- The position of drain
- Other abnormalities (emphyema, shadow mediastonim)
1. The number on the bottle sekrit shelters should be calculated:
- Many sekrit out (every hour - every day)
- Kinds sekrit out (pus, blood, etc.)
1. In patients with respiratory physiotherapy has always done
2. Any abnormalities in the drain should be immediately corrected.
Revocation guidelines
1. Criteria for revocation
- Sekrit serous, not hemorage
Adults: the amount is less than 100cc/24jam
Children - children: less number 25-50cc/24jam
- Lung expands
Clinical; sound right = left lung expands
Evaluation of chest X-ray
1. Condition:
- In the trauma
Hemato / pneumothorak who already meet both criteria, immediately revoked by the water-tight (air tight).
- In thoracotomi
a. Infection: 24h clamps to prevent resufflasi first, if either unplug.
b. Post operative: if it fulfills both criteria, langsug revoked (water-tight)
c. Post pneumonectomy: day-to-3 when the mediastinum is stable (does not need water-tight
1. Alternative
1. Permanent lung collapse, suction up to 25 cmH20:
- If both krieria met, the clamps first 24 hours, fixed baikà unplug.
- If unsuccessful, wait until 2minggu à dekortikasi
1.
1. Sekrit over 200cc/24jam: suspicion of thoracic Chylo (make sure the laboratory), keep up with 4minggu.
- If unsuccessful à Toracotomi
- If less than 100cc/24jam sekrit, clamps, and then revoked.Follow - Up
Aimed at the onset of further complications such as empyema, Schwarte, impaired respiratory function.
Repair Injuries Peripheral Nerve
Introduction
a. Definition
Repair of peripheral nerve injury is a surgery that aims to improve peripheral nerve injury.
b. Scope
Peripheral nerve injury both open and closed frequently encountered a surgeon. Principle - general principles in dealing with peripheral nerve injury based upon a good understanding of basic biological-daasr nervous system and its response to trauma.
Traditional classification of peripheral nerve injury is klasifiaksi Seddon. Seddon describes the three kinds of injuries are: neuropraksia, axonotmesis and neuotmesis.
Neuropraxia
Is non-functioning of the nervous system without the occurrence of a temporary physical disruption of axons. Usually the nerve function will return to normal after 2-4 weeks.
Axonotmesis
Is the disruption of axons and myelin. Yes sekitarn soft connective tissue including intact endoneurium. Axon degeneration occurs distal and proximal location of the trauma. Distal degeneration known as Wallerian degeneration. Axon regeneration will memngalami with speed 1mm / day. Significantly the function will return to normal after 18 months.
Neurotmesis
Is the disruption of axons and endoneurial. Peripheral components such as collagen can epineurium intact or disruption occur. Axonal degeneration occurs in the distal and proximal segments.
c. Operation Indication
* Complete nerve lesions caused by lacerations or penetrating injuries
* Other nerve lesions are quite meaningful without clinical or electrophysiological improvement after 3-6 months of clinical observation
d. Contra indications of operation (no)
d. Diagnoses
Acute inflammatory demyelinating * · Polyradiculoneuropathy
* · Cervical Spondylosis: Diagnosis and Management
* · Diabetic Neuropathy
* · Femoral Mononeuropathy
* · Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Childhood
* · HIV-1 Associated Acute / Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
* · HIV-1 Associated Distal Painful sensorimotor polyneuropathy
* · HIV-1 Associated Multiple Mononeuropathies
* · HIV-1 Associated Neuromuscular Complications (Overview)
* · Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis
* · Metastatic disease to the Spine and Related Structures
* · Peroneal Mononeuropathy
* · Polyarteritis nodosa
* · Radial Mononeuropathy
* · Spinal Cord Hemorrhage
* · Spinal Cord Infarction
* · Syringomyelia
* · Vasculitic Neuropathy
e. Examination Support
EMG (Elektromyografi)
Engineering Operations
Operating techniques that can be applied to peripheral nerve repair include internal and external neurolisis. External Neurolisis done by freeing the nerve from surrounding tissues are circumferential. Internal Neurolisis indicated for partial nerve lesions that require separate reparations between fasikulus fasikulus nerve functioning nerve is not functioning. This procedure has the potential to injure the axons to regenerate and be done with electrophysiological guidance. In general, the internal neurolisis dissection segment includes non fungional. Then fasikulus already made reparations didiseksi end to end with or without a nerve graft.
Reparations end to end is preferred that occurs when a small gap and both ends can be brought near without stress / tension meaningful. Tension will hinder the healing process. If a considerable distance, it can be done graft interposition. Generally the donor nerve is taken from the superficial sensory nerves such as autologous nerve suralis. Monofilament suture (7.0 to 10.0) in the epineurium is used to bring fasikulus. Nerve ends should be resected to healthy fasikulus to get a good orientation and optimize repair functions. Yet continuity fasikulus anatomically not guarantee the regeneration of axons. Two causes of the failure is not good preparation and a tension-laden stump. Secondly it will cause the occurrence of scar interneural sarabut that would interfere with nerve regeneration.
Complications of surgery
Anastomosis failure
Mortality (none)
Postoperative care
After the occurrence of peripheral nerve injury, it is essential that patients have to undergo physiotherapy to maintain ROM and to prevent immobilization to optimize healing of motor function in conjunction with the occurrence of muscle reinervasi.
Follow-up
EMG monitoring is helpful to detect early signs of muscle reinervasi few months before the contraction is clinically available.
a. Definition
Repair of peripheral nerve injury is a surgery that aims to improve peripheral nerve injury.
b. Scope
Peripheral nerve injury both open and closed frequently encountered a surgeon. Principle - general principles in dealing with peripheral nerve injury based upon a good understanding of basic biological-daasr nervous system and its response to trauma.
Traditional classification of peripheral nerve injury is klasifiaksi Seddon. Seddon describes the three kinds of injuries are: neuropraksia, axonotmesis and neuotmesis.
Neuropraxia
Is non-functioning of the nervous system without the occurrence of a temporary physical disruption of axons. Usually the nerve function will return to normal after 2-4 weeks.
Axonotmesis
Is the disruption of axons and myelin. Yes sekitarn soft connective tissue including intact endoneurium. Axon degeneration occurs distal and proximal location of the trauma. Distal degeneration known as Wallerian degeneration. Axon regeneration will memngalami with speed 1mm / day. Significantly the function will return to normal after 18 months.
Neurotmesis
Is the disruption of axons and endoneurial. Peripheral components such as collagen can epineurium intact or disruption occur. Axonal degeneration occurs in the distal and proximal segments.
c. Operation Indication
* Complete nerve lesions caused by lacerations or penetrating injuries
* Other nerve lesions are quite meaningful without clinical or electrophysiological improvement after 3-6 months of clinical observation
d. Contra indications of operation (no)
d. Diagnoses
Acute inflammatory demyelinating * · Polyradiculoneuropathy
* · Cervical Spondylosis: Diagnosis and Management
* · Diabetic Neuropathy
* · Femoral Mononeuropathy
* · Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Childhood
* · HIV-1 Associated Acute / Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
* · HIV-1 Associated Distal Painful sensorimotor polyneuropathy
* · HIV-1 Associated Multiple Mononeuropathies
* · HIV-1 Associated Neuromuscular Complications (Overview)
* · Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis
* · Metastatic disease to the Spine and Related Structures
* · Peroneal Mononeuropathy
* · Polyarteritis nodosa
* · Radial Mononeuropathy
* · Spinal Cord Hemorrhage
* · Spinal Cord Infarction
* · Syringomyelia
* · Vasculitic Neuropathy
e. Examination Support
EMG (Elektromyografi)
Engineering Operations
Operating techniques that can be applied to peripheral nerve repair include internal and external neurolisis. External Neurolisis done by freeing the nerve from surrounding tissues are circumferential. Internal Neurolisis indicated for partial nerve lesions that require separate reparations between fasikulus fasikulus nerve functioning nerve is not functioning. This procedure has the potential to injure the axons to regenerate and be done with electrophysiological guidance. In general, the internal neurolisis dissection segment includes non fungional. Then fasikulus already made reparations didiseksi end to end with or without a nerve graft.
Reparations end to end is preferred that occurs when a small gap and both ends can be brought near without stress / tension meaningful. Tension will hinder the healing process. If a considerable distance, it can be done graft interposition. Generally the donor nerve is taken from the superficial sensory nerves such as autologous nerve suralis. Monofilament suture (7.0 to 10.0) in the epineurium is used to bring fasikulus. Nerve ends should be resected to healthy fasikulus to get a good orientation and optimize repair functions. Yet continuity fasikulus anatomically not guarantee the regeneration of axons. Two causes of the failure is not good preparation and a tension-laden stump. Secondly it will cause the occurrence of scar interneural sarabut that would interfere with nerve regeneration.
Complications of surgery
Anastomosis failure
Mortality (none)
Postoperative care
After the occurrence of peripheral nerve injury, it is essential that patients have to undergo physiotherapy to maintain ROM and to prevent immobilization to optimize healing of motor function in conjunction with the occurrence of muscle reinervasi.
Follow-up
EMG monitoring is helpful to detect early signs of muscle reinervasi few months before the contraction is clinically available.
Repair Hypospadias
Introduction
a. Definition
An abnormal state of development of the anterior urethra where the external urethral meatus located on the ventral and is located more proximal than the normal location and was accompanied on the distal part of firosis MUE that cause crooked penis (chordae).
b. Scope
Hypospadias in the distal, midshaft and proximal penis.
c. Operation Indication
The purpose hypospadias surgery is to straighten the penis, allowing the process of micturition while standing and to increase fertility.
d. Contra indications of operation (no)
e. Differential diagnosis (no)
f. Examination Support
Only by clinical examination
Engineering Operations
Optimal operating time is when children aged 3 to 18 months. At this time children will have amnesia of the surgical procedure and 70-80% of abnormalities can be handled without the need to be treated.
There are two stages of hypospadias surgery, the first is the excision Korde and tunneling, and the second is the reconstruction of the urethra (uretroplasty)
Excision Korde
After incision of hypospadias has been done and the flap has been lifted, the entire network can result in bent lifted from around the meatus, and below the glans. After the artificial erection test was performed. When Korde persists, then further resection is required.
Urethroplasty
There are many techniques that can be used for urethroplasty, but that will be discussed is a fairly common technique used MAGPI.
MAGPI (meatal Advancement and Glanuloplasty Incorporated)
MAGPI technique can be used for patients with distal hypospadias glanular. Once the penis is seen straight on artificial erection test, sirkumsis incision performed. Skin hooks are placed at the edge of the end of the channel glanular urethra and then withdrawn to the lateral direction. This movement can increase the transverse bands of the mucosa which will be a longitudinal incision in the midline. Incision on the dorsal wall of the urethra glanular dengna would eventually be closed with chromic catgut sutures transverse 6-0. Skin hooks are placed on the skin edges of the corona at the ventral midline. With traction distally, tip of the glans is pulled forward and stitched on the midline with sutures subkutikuler. Epithelium of the glans was closed with interrupted sutures. Excess skin of the dorsal prepusium be sewn to skin closure.
Complications Surgery
Short-term
* Local edema and hemorrhage bintk spots can occur immediately after surgery and usually do not cause significant problems
* Postoperative Hemorrhage is rare and can usually be controlled dengna dressing press. Not infrequently this requires re-exploration to remove the hematoma and to identify and address the source of bleeding.
* Infection is a fairly rare complication of hypospadias. With skin preparation and perioperative antibiotics this can be prevented.
Long-term
* Fistula: Fistula uretrokutan is a major problem that often arises in the operation hpospadia. Fistulas rarely close spontaneously and can be repaired dengna layered closure of a local skin flap.
* Meatus stenosis: stenosis or narrowing of the urethral meatus may occur. The flow of urine which can lead to reduced vigilance over the meatus stenosis.
* Stricture: This condition can develop as long-term complications of hypospadias surgery. This situation can be corrected with surgery, and may require an incision, excision or reanastomosis.
* Diverticula: Urethral Diverticula can also form characterized by the development of the urethra during urination. Stricture at the distal obstruction can result in the flow and ended in urethral diverticula. Diverticula can form even though there is no obstruction in the distal part. This can occur related to the graft or flap in hypospadias surgery, which propped up of muscle and subcutaneous tissue from the urethra of origin.
* The presence of hair on the urethra: The skin containing hair follicles used in the reconstruction of hypospadias be avoided. When the skin is associated * with the urethra, this can cause problems in the form of urinary tract infection and stone formation during puberty. Usually to solve a laser or cautery is used, even if pretty much done on the excision of skin containing hair follicles and then repeated hypospadias repair.
Mortality
Very low
Postoperative treatment
- Day-3 post-operative care performed with a removable splint injuries
- Maintain a urinary catheter ± 10-14 days post-surgery
Follow Up
After surgery patients were given a cold compress on the area of operations during the first 2 days. This method can reduce edema and pain as well as keeping the area clean operation. Patients who use suprapubic catheter, urethral sten may also require a small and may be revoked on the fifth postoperative day. In patients who use the tube graft or flap prepusium, micturition process is done through percutaneous suprapubic catheter. Depending on the wound healing process, the catheter was closed on day 10 for experiment micturition. If there is difficulty in this method was repeated 3-4 days later. If up to 3 weeks the fistula persists, micturition process continued as usual after the patient disarankkan to improve operating results 6 months later when the inflammatory process has disappeared. Usually a small fistula may close spontaneously.
After the trial micturition, the patient can bathe as usual. Dressing can be separated spontaneously. After the release of sten, parents were asked to keep the meatus remain open using Neosporin eye ointment jar lid so that the crust at the meatus does not cause an obstruction distal to develop into a fistula.
a. Definition
An abnormal state of development of the anterior urethra where the external urethral meatus located on the ventral and is located more proximal than the normal location and was accompanied on the distal part of firosis MUE that cause crooked penis (chordae).
b. Scope
Hypospadias in the distal, midshaft and proximal penis.
c. Operation Indication
The purpose hypospadias surgery is to straighten the penis, allowing the process of micturition while standing and to increase fertility.
d. Contra indications of operation (no)
e. Differential diagnosis (no)
f. Examination Support
Only by clinical examination
Engineering Operations
Optimal operating time is when children aged 3 to 18 months. At this time children will have amnesia of the surgical procedure and 70-80% of abnormalities can be handled without the need to be treated.
There are two stages of hypospadias surgery, the first is the excision Korde and tunneling, and the second is the reconstruction of the urethra (uretroplasty)
Excision Korde
After incision of hypospadias has been done and the flap has been lifted, the entire network can result in bent lifted from around the meatus, and below the glans. After the artificial erection test was performed. When Korde persists, then further resection is required.
Urethroplasty
There are many techniques that can be used for urethroplasty, but that will be discussed is a fairly common technique used MAGPI.
MAGPI (meatal Advancement and Glanuloplasty Incorporated)
MAGPI technique can be used for patients with distal hypospadias glanular. Once the penis is seen straight on artificial erection test, sirkumsis incision performed. Skin hooks are placed at the edge of the end of the channel glanular urethra and then withdrawn to the lateral direction. This movement can increase the transverse bands of the mucosa which will be a longitudinal incision in the midline. Incision on the dorsal wall of the urethra glanular dengna would eventually be closed with chromic catgut sutures transverse 6-0. Skin hooks are placed on the skin edges of the corona at the ventral midline. With traction distally, tip of the glans is pulled forward and stitched on the midline with sutures subkutikuler. Epithelium of the glans was closed with interrupted sutures. Excess skin of the dorsal prepusium be sewn to skin closure.
Complications Surgery
Short-term
* Local edema and hemorrhage bintk spots can occur immediately after surgery and usually do not cause significant problems
* Postoperative Hemorrhage is rare and can usually be controlled dengna dressing press. Not infrequently this requires re-exploration to remove the hematoma and to identify and address the source of bleeding.
* Infection is a fairly rare complication of hypospadias. With skin preparation and perioperative antibiotics this can be prevented.
Long-term
* Fistula: Fistula uretrokutan is a major problem that often arises in the operation hpospadia. Fistulas rarely close spontaneously and can be repaired dengna layered closure of a local skin flap.
* Meatus stenosis: stenosis or narrowing of the urethral meatus may occur. The flow of urine which can lead to reduced vigilance over the meatus stenosis.
* Stricture: This condition can develop as long-term complications of hypospadias surgery. This situation can be corrected with surgery, and may require an incision, excision or reanastomosis.
* Diverticula: Urethral Diverticula can also form characterized by the development of the urethra during urination. Stricture at the distal obstruction can result in the flow and ended in urethral diverticula. Diverticula can form even though there is no obstruction in the distal part. This can occur related to the graft or flap in hypospadias surgery, which propped up of muscle and subcutaneous tissue from the urethra of origin.
* The presence of hair on the urethra: The skin containing hair follicles used in the reconstruction of hypospadias be avoided. When the skin is associated * with the urethra, this can cause problems in the form of urinary tract infection and stone formation during puberty. Usually to solve a laser or cautery is used, even if pretty much done on the excision of skin containing hair follicles and then repeated hypospadias repair.
Mortality
Very low
Postoperative treatment
- Day-3 post-operative care performed with a removable splint injuries
- Maintain a urinary catheter ± 10-14 days post-surgery
Follow Up
After surgery patients were given a cold compress on the area of operations during the first 2 days. This method can reduce edema and pain as well as keeping the area clean operation. Patients who use suprapubic catheter, urethral sten may also require a small and may be revoked on the fifth postoperative day. In patients who use the tube graft or flap prepusium, micturition process is done through percutaneous suprapubic catheter. Depending on the wound healing process, the catheter was closed on day 10 for experiment micturition. If there is difficulty in this method was repeated 3-4 days later. If up to 3 weeks the fistula persists, micturition process continued as usual after the patient disarankkan to improve operating results 6 months later when the inflammatory process has disappeared. Usually a small fistula may close spontaneously.
After the trial micturition, the patient can bathe as usual. Dressing can be separated spontaneously. After the release of sten, parents were asked to keep the meatus remain open using Neosporin eye ointment jar lid so that the crust at the meatus does not cause an obstruction distal to develop into a fistula.
Extremity Amputation Techniques
a. The basic principle of amputation
With advances in the field of prostheses is the selection of the amputation in order to maintain the limb sedistal may not be entirely correct. This applies to the superior limb amputation. Rules which states for limb mempretahankan sedistal may not be applicable to the inferior extremity amputation. Even so far as possible the knee must be saved, because the knee is very useful functionally. Problem of weight bearing and leaves soft tissue to cover the stump greatly influence the selection of the amputation of the inferior ekstremias. In below knee amputation stump that is too long is not advised because it would complicate the use of the prosthesis. Anterior border of the tibia should be available in the bevel and enough soft tissue to cover it by making a flap diposterior longer. Amputation of ankle-high enough indication has rarely, usually in trauma. Syme amputation is useful for end weight bearing prosthesis. For amputation of the foot is general agreement that is used is trans metatarsal (the level of amputation see schematic drawing).
Location to perform an amputation:
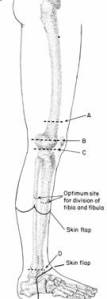





With advances in the field of prostheses is the selection of the amputation in order to maintain the limb sedistal may not be entirely correct. This applies to the superior limb amputation. Rules which states for limb mempretahankan sedistal may not be applicable to the inferior extremity amputation. Even so far as possible the knee must be saved, because the knee is very useful functionally. Problem of weight bearing and leaves soft tissue to cover the stump greatly influence the selection of the amputation of the inferior ekstremias. In below knee amputation stump that is too long is not advised because it would complicate the use of the prosthesis. Anterior border of the tibia should be available in the bevel and enough soft tissue to cover it by making a flap diposterior longer. Amputation of ankle-high enough indication has rarely, usually in trauma. Syme amputation is useful for end weight bearing prosthesis. For amputation of the foot is general agreement that is used is trans metatarsal (the level of amputation see schematic drawing).
Location to perform an amputation:






b. Operation indication
* Trauma
* Dead ganggan limb due to vascular supply
* Malignant neoplasms
* Chronic Osteomyelitis
* Life-threatening infections
* Congenital limb deformities are inoperable
c. Contra indications of operation: the general state of poor
Engineering Operations
Management of Extremity Amputation
Anesthesia
Spinal anesthesia is commonly used for lower extremity amputations, anstesia common for upper limb amputation. Can also be used leksus block anesthesia. Amputation of the finger can be used for local infiltration anesthesia.
Mechanical operation
Above-knee amputation
The best place to split the femur is 8-10 cm (the width of one hand). Use of skin markers to plan the incision, which should create a flap of anterior and posterior flaps have the same length or slightly longer anteriorly. For those of skin and subcutaneous tissue along the line are planned. Hemostasis is usually not difficult in the ischemic limb but severe bleeding can occur in the limbs are septic. Tie all of veins by using absorbent needle 2 / 0. The anterior incision is deepened to the bone, cutting the quadriceps femoris tendon. Vasa femoral together media and lateral popliteal nerves found in posteromedial position. Tie with thread veins double absorbency. Before cutting the nerve, give stress on the nerve so nerve interested in the amputation stump. If the amputation performed at a higher level, sciaticus nerve can be found. Sciaticus nerve followed by the artery to be didiseksi separately and fastened prior to nerve cut. After cutting all the muscles around the femur, the living tissue vessels and avoid the use of diathermy. Check the exact point of amputation of the femur and scrape the periosteum from the bone in this area. The muscles of the thighs must be retracted to the proximal direction to provide sufficient space in the use of chainsaws. This can be done with the help of some abdominal pads or special retractors. After cutting off the femur and lower leg, place a clean towel under the butt and rest your butt on the inverted bowl. Use stingy to smooth the edge of the femur, then bring the muscles along the front and back cover cut off the bone with suture thread absorbency size 1. Attach suction drain the skin incision below the point of cutting the bone in the muscle layer. Place the second layer of stitches is more superficial in the muscle and subcutaneous tissue as this will help close the flap of skin. Sew the edge of the skin with stitches broke up with non-absorbent yarn 2 / 0. Avoid picking the edge of the skin with toothed forceps. Close stump with gauze and cotton and dressing with crepe bandage.
Below-knee amputation
Optimum point for amputation is 14 cm from the tibial plateau, the fibula was cut 2 cm proximal from this. Tick incision, with anterior flap ends just distal of the cutting line on the tibia bone and the posterior flap extends down to the Achilles tendon. Make an incision along the lines that have been marked. In the posterior Achilles tendon cut and deepen the incision to cut the rest of the muscles and tendons to bone. Cut across the muscle into up front. Fibular oblique cut with a saw Gigli, then split the tibia 2 cm distal to this. Clean the muscle from the bone with periosteum elevator. Cut the anterior bevel first with a saw and cut perpendicular to the diagonal of the tibia. Forms angle at the lower end of the tibia towards the top and separate the muscle mass of the posterior aspect. Tie a double all the blood vessels and cut every nerve tense. Remove the distal limb. The posterior flap is pulled upward to wrap butt bone and sutured to the anterior flap. Posterior flap may need to be reduced by excision of muscle tissue. Place absorbent yarn in between the muscles in the posterior and anterior subcutaneous tissue and leave the suction drain beneath the muscle. Bring the edge of the skin with stitches drop out of non-absorbent yarn 2 / 0. Snip the corners of the posterior flap if necessary in order to form neat. Close the butt with a tight bandage with cotton and crepe bandage.
Complications of surgery
* Bleeding
* Infection
Mortality
Depending on the etiology
* Dead ganggan limb due to vascular supply
* Malignant neoplasms
* Chronic Osteomyelitis
* Life-threatening infections
* Congenital limb deformities are inoperable
c. Contra indications of operation: the general state of poor
Engineering Operations
Management of Extremity Amputation
Anesthesia
Spinal anesthesia is commonly used for lower extremity amputations, anstesia common for upper limb amputation. Can also be used leksus block anesthesia. Amputation of the finger can be used for local infiltration anesthesia.
Mechanical operation
Above-knee amputation
The best place to split the femur is 8-10 cm (the width of one hand). Use of skin markers to plan the incision, which should create a flap of anterior and posterior flaps have the same length or slightly longer anteriorly. For those of skin and subcutaneous tissue along the line are planned. Hemostasis is usually not difficult in the ischemic limb but severe bleeding can occur in the limbs are septic. Tie all of veins by using absorbent needle 2 / 0. The anterior incision is deepened to the bone, cutting the quadriceps femoris tendon. Vasa femoral together media and lateral popliteal nerves found in posteromedial position. Tie with thread veins double absorbency. Before cutting the nerve, give stress on the nerve so nerve interested in the amputation stump. If the amputation performed at a higher level, sciaticus nerve can be found. Sciaticus nerve followed by the artery to be didiseksi separately and fastened prior to nerve cut. After cutting all the muscles around the femur, the living tissue vessels and avoid the use of diathermy. Check the exact point of amputation of the femur and scrape the periosteum from the bone in this area. The muscles of the thighs must be retracted to the proximal direction to provide sufficient space in the use of chainsaws. This can be done with the help of some abdominal pads or special retractors. After cutting off the femur and lower leg, place a clean towel under the butt and rest your butt on the inverted bowl. Use stingy to smooth the edge of the femur, then bring the muscles along the front and back cover cut off the bone with suture thread absorbency size 1. Attach suction drain the skin incision below the point of cutting the bone in the muscle layer. Place the second layer of stitches is more superficial in the muscle and subcutaneous tissue as this will help close the flap of skin. Sew the edge of the skin with stitches broke up with non-absorbent yarn 2 / 0. Avoid picking the edge of the skin with toothed forceps. Close stump with gauze and cotton and dressing with crepe bandage.
Below-knee amputation
Optimum point for amputation is 14 cm from the tibial plateau, the fibula was cut 2 cm proximal from this. Tick incision, with anterior flap ends just distal of the cutting line on the tibia bone and the posterior flap extends down to the Achilles tendon. Make an incision along the lines that have been marked. In the posterior Achilles tendon cut and deepen the incision to cut the rest of the muscles and tendons to bone. Cut across the muscle into up front. Fibular oblique cut with a saw Gigli, then split the tibia 2 cm distal to this. Clean the muscle from the bone with periosteum elevator. Cut the anterior bevel first with a saw and cut perpendicular to the diagonal of the tibia. Forms angle at the lower end of the tibia towards the top and separate the muscle mass of the posterior aspect. Tie a double all the blood vessels and cut every nerve tense. Remove the distal limb. The posterior flap is pulled upward to wrap butt bone and sutured to the anterior flap. Posterior flap may need to be reduced by excision of muscle tissue. Place absorbent yarn in between the muscles in the posterior and anterior subcutaneous tissue and leave the suction drain beneath the muscle. Bring the edge of the skin with stitches drop out of non-absorbent yarn 2 / 0. Snip the corners of the posterior flap if necessary in order to form neat. Close the butt with a tight bandage with cotton and crepe bandage.
Complications of surgery
* Bleeding
* Infection
Mortality
Depending on the etiology
Postoperative care and follow-up
* Wound care in general
* Rehabilitation of the manufacture of a suitable prosthesis
* Rehabilitation of the manufacture of a suitable prosthesis
EKSKOKLEASI cyst JAW
a. Definition
An action pengerokan mucous cyst wall is concerned with tooth extraction, removal of the protruding cyst wall.
b. Scope
Odontogenic cysts are non-neoplastic cysts of the mandible or maxilla, ie when the tooth root cyst radicular cyst is facing, and follicular cysts when the cyst is facing dental crowns
c. Indications of surgery
All follicular and radicular cysts
d. Contra indications Operations
Ko severe morbidity
e. Diagnoses
Ameblastoma unilokuler
f. Investigations
Photos of the mandible (Eisler, Panoramic, Hap) photo maxillary (Waters, Hap) depending on location
Engineering Operations
Ahead of the operation:
Explanation to the patient and his family about his illness, surgery and the risk of complications is accompanied by the signature of approval and requests from patients for surgery. (Informed consent). Check and complete the preparation of tools and completeness of the operation including yarn, Redon drain done the day before surgery.
Patients with fasting at least 6 hours before surgery.
Patients with a shower, washing hair and cleaning the body using an antiseptic drugs, especially the face and the hair near the operating field, shaving the hair close to the operating field, sideburns, mustache.
Antibiotic prophylaxis with Cefazolin or clindamycin combination Garamycin, adjusting doses for prophylaxis.
Stages of operation:
Narcotics, nasotrakheal intubation, intubation tubes were fixed to the patient's forehead.
Position the patient supine, with a padded donut on the head.
Incision bukogingival cysts on the prominent areas.
Incision is deepened until it reached the wall of the cyst is made sufficiently mucosal flap, partial cyst wall excised elliptical shape. The mucosa that lines the inner surface scraped clean and the cyst removed.
Apply a paste or tooth extraction into the cyst.
Attach with ribbon gauze tampon into the cavity of the cyst, tampons were fixed to the mucosa using 3.0 silk, then surgical wound or mucosa sutured with vicryl 3.0 dexon a knot.
Complications Surgery
Early Postoperative Complications
Hematoma, will increase the risk of wound infection and dehisensi. Control of bleeding is good and the tent will reduce the risk of hematoma
Infection, minimized by avoiding the buildup of fluid, with the tent. Operational planning and good surgical technique also plays a role in controlling the infection in addition to the use of prophylactic antibiotics.
Mortality
Low Mortality
Post-Surgical Care
* Provision of adequate intravenous fluids.
* Antibiotic prophylaxis is continued until 3 days post-surgery
* Fasting for 2 days.
* Gargle with antiseptic solution.
* Tampons detachable day 3
Follow-Up
Control every 3 months for 1 year
An action pengerokan mucous cyst wall is concerned with tooth extraction, removal of the protruding cyst wall.
b. Scope
Odontogenic cysts are non-neoplastic cysts of the mandible or maxilla, ie when the tooth root cyst radicular cyst is facing, and follicular cysts when the cyst is facing dental crowns
c. Indications of surgery
All follicular and radicular cysts
d. Contra indications Operations
Ko severe morbidity
e. Diagnoses
Ameblastoma unilokuler
f. Investigations
Photos of the mandible (Eisler, Panoramic, Hap) photo maxillary (Waters, Hap) depending on location
Engineering Operations
Ahead of the operation:
Explanation to the patient and his family about his illness, surgery and the risk of complications is accompanied by the signature of approval and requests from patients for surgery. (Informed consent). Check and complete the preparation of tools and completeness of the operation including yarn, Redon drain done the day before surgery.
Patients with fasting at least 6 hours before surgery.
Patients with a shower, washing hair and cleaning the body using an antiseptic drugs, especially the face and the hair near the operating field, shaving the hair close to the operating field, sideburns, mustache.
Antibiotic prophylaxis with Cefazolin or clindamycin combination Garamycin, adjusting doses for prophylaxis.
Stages of operation:
Narcotics, nasotrakheal intubation, intubation tubes were fixed to the patient's forehead.
Position the patient supine, with a padded donut on the head.
Incision bukogingival cysts on the prominent areas.
Incision is deepened until it reached the wall of the cyst is made sufficiently mucosal flap, partial cyst wall excised elliptical shape. The mucosa that lines the inner surface scraped clean and the cyst removed.
Apply a paste or tooth extraction into the cyst.
Attach with ribbon gauze tampon into the cavity of the cyst, tampons were fixed to the mucosa using 3.0 silk, then surgical wound or mucosa sutured with vicryl 3.0 dexon a knot.
Complications Surgery
Early Postoperative Complications
Hematoma, will increase the risk of wound infection and dehisensi. Control of bleeding is good and the tent will reduce the risk of hematoma
Infection, minimized by avoiding the buildup of fluid, with the tent. Operational planning and good surgical technique also plays a role in controlling the infection in addition to the use of prophylactic antibiotics.
Mortality
Low Mortality
Post-Surgical Care
* Provision of adequate intravenous fluids.
* Antibiotic prophylaxis is continued until 3 days post-surgery
* Fasting for 2 days.
* Gargle with antiseptic solution.
* Tampons detachable day 3
Follow-Up
Control every 3 months for 1 year
Repair Volvulus
Repair Volvulus is a surgery to reposition bowel torsion (volvulus).
Volvulus is a condition characterized by severe abdominal pain is colicky abdominal colic attacks there in which the persistent abdominal pain, abdominal bloating due to abdominal distension is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
There is a picture of a typical x-ray photograph image of a car tire with great curves and where examination using a slurry of barium x-ray photograph the bird's beak looks a picture.
Indications of surgery
* Strangulation
Contra indications operation
* People with bad general condition
Differential diagnosis
* Carcinoma of colon
* Diverticulitis
* Stricture rectum
* Hirschsprung Disease
Investigations
* Plain abdominal
* Photo of barium
Engineering Operations
Management
In principle there are two management volvulus, namely:
I. Operation
Surgical technique depends on the kind of volvulus:
1. Cecum volvulus
Resection performed with ileokolostomi terminolateral ileosekal
2. Sigmoid volvulus
Generally done with anastomosis sigmoidektomi terminal terminology but if circumstances do not generally allow for primary anastomosis can be performed Hartmann's procedure (resection of the sigmoid colon with end kolokutoneostomi oral and anal colonic end closing). After the general state of the new permit be done by eliminating kolokutoneostomi kolokolostomi anastomosis. If things do not generally allow enough detorsi, then fixation of the sigmoid (sigmoidopeksi).
II. Non-operating
Action with rektoskop decompression, colonoscope or flexible pipe.
Complications of surgery
Action sigmoid fixation (sigmoidopeksi) raises recurrence of 90% is also in action with rektoskop decompression, colonoscope or flexible pipes cause of recurrence 40-70%.
Mortality
Decompression with rektoskop action, colonoscope or flexible pipe has a low mortality rate is 5-8% while the actions of resection / kolopeksi have a high mortality rate of 0-22%.
Post-Surgical Care
* Maintain nosogastric 1-3 days
* Diet orally administered after functioning digestive tract begins with a liquid diet that is gradually given soft food and solid
* Actual as early as possible
Volvulus is a condition characterized by severe abdominal pain is colicky abdominal colic attacks there in which the persistent abdominal pain, abdominal bloating due to abdominal distension is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
There is a picture of a typical x-ray photograph image of a car tire with great curves and where examination using a slurry of barium x-ray photograph the bird's beak looks a picture.
Indications of surgery
* Strangulation
Contra indications operation
* People with bad general condition
Differential diagnosis
* Carcinoma of colon
* Diverticulitis
* Stricture rectum
* Hirschsprung Disease
Investigations
* Plain abdominal
* Photo of barium
Engineering Operations
Management
In principle there are two management volvulus, namely:
I. Operation
Surgical technique depends on the kind of volvulus:
1. Cecum volvulus
Resection performed with ileokolostomi terminolateral ileosekal
2. Sigmoid volvulus
Generally done with anastomosis sigmoidektomi terminal terminology but if circumstances do not generally allow for primary anastomosis can be performed Hartmann's procedure (resection of the sigmoid colon with end kolokutoneostomi oral and anal colonic end closing). After the general state of the new permit be done by eliminating kolokutoneostomi kolokolostomi anastomosis. If things do not generally allow enough detorsi, then fixation of the sigmoid (sigmoidopeksi).
II. Non-operating
Action with rektoskop decompression, colonoscope or flexible pipe.
Complications of surgery
Action sigmoid fixation (sigmoidopeksi) raises recurrence of 90% is also in action with rektoskop decompression, colonoscope or flexible pipes cause of recurrence 40-70%.
Mortality
Decompression with rektoskop action, colonoscope or flexible pipe has a low mortality rate is 5-8% while the actions of resection / kolopeksi have a high mortality rate of 0-22%.
Post-Surgical Care
* Maintain nosogastric 1-3 days
* Diet orally administered after functioning digestive tract begins with a liquid diet that is gradually given soft food and solid
* Actual as early as possible
Orchidopexi / Orchidektomi In Undescencus testes (UDT)
a. definition
A surgery in the form of laying the testis in the proper place
b. scope
UDT is a situation where the testes are not in place correspond inguinal line. UDT Signs of no palpable testes in the scrotum, testes palpable in the area ingunal.
c. indications of surgery
UDT
d. Contra indications of operation:
general
Special (inoperable)
e. Diagnoses (none)
f. examination Support
abdominal ultrasound
Technical Operations
In later stages of anesthesia, supine position, the groin and scrotum is cleaned with antiseptic solution. Incision is made in the groin in areas of UDT. MOE apponerosis Kemidian opened up to look funikulus spermatikus gubernaculum testis is identified then cut, procecus vaginalis peritonii ditordir and tied seproksimal possible. Testicular freed from surrounding connective tissue to look at long-Cort testicle scrotum can achieve with the help of a finger pushing the tunica dartos reach the scrotum. Then inserted into the testes were fixed in the tunica dartos and the scrotal skin. Surgical wound was closed layer by layer.
complications of surgery
Bleeding, it is currently rare.
mortality
Less than 1%
postoperative care
Post-surgical patients treated for 1 day, observed the possibility of life-threatening complications such as bleeding patients. Antibiotics and analgesics
A surgery in the form of laying the testis in the proper place
b. scope
UDT is a situation where the testes are not in place correspond inguinal line. UDT Signs of no palpable testes in the scrotum, testes palpable in the area ingunal.
c. indications of surgery
UDT
d. Contra indications of operation:
general
Special (inoperable)
e. Diagnoses (none)
f. examination Support
abdominal ultrasound
Technical Operations
In later stages of anesthesia, supine position, the groin and scrotum is cleaned with antiseptic solution. Incision is made in the groin in areas of UDT. MOE apponerosis Kemidian opened up to look funikulus spermatikus gubernaculum testis is identified then cut, procecus vaginalis peritonii ditordir and tied seproksimal possible. Testicular freed from surrounding connective tissue to look at long-Cort testicle scrotum can achieve with the help of a finger pushing the tunica dartos reach the scrotum. Then inserted into the testes were fixed in the tunica dartos and the scrotal skin. Surgical wound was closed layer by layer.
complications of surgery
Bleeding, it is currently rare.
mortality
Less than 1%
postoperative care
Post-surgical patients treated for 1 day, observed the possibility of life-threatening complications such as bleeding patients. Antibiotics and analgesics
Circumcision in phimosis
Introductions:
a. definition
A surgery is a form of disposal of penis prepuce
b. scope
Phimosis is a condition where the penis prepuce can not be withdrawn so that the glans penis is not visible. Occurs because kongeniatl or acquired abnormalities. At gained largely because balanopostitis
c. indications of surgery
Obtruksi, balanopostitis
d. Contra indications of operation:
general
Special (inoperable)
e. Diagnoses (none)
f. Examination Support (no)
Technical Operations
Briefly circumcision surgery techniques can be explained as follows:
After the patient was given narcotics, place the patient in the supine position. Disinfection with an antiseptic surgical field then narrowed with sterile linen. Prepuce in the wash with antiseptic fluid around the glans penis. Preputium the clamps on the 3 spot. Preputium the scissors on the dorsal side of the penis to the limit glandis corona. Created teugel at the end of the incision. The same Teugel done on frenulum penis. Preputium then cut a circle parallel to the corona glandis. Then the skin and mucosa sutured with plain gut 4.0 atraumatic interupted cut.
complications of surgery
Bleeding, it is currently rare.
Mortality (none)
postoperative care
Post-surgical patients can be directly outpatient, observed the possibility of people with life-threatening complication such as antibiotics and analgesics perdarahan.Pemberian
a. definition
A surgery is a form of disposal of penis prepuce
b. scope
Phimosis is a condition where the penis prepuce can not be withdrawn so that the glans penis is not visible. Occurs because kongeniatl or acquired abnormalities. At gained largely because balanopostitis
c. indications of surgery
Obtruksi, balanopostitis
d. Contra indications of operation:
general
Special (inoperable)
e. Diagnoses (none)
f. Examination Support (no)
Technical Operations
Briefly circumcision surgery techniques can be explained as follows:
After the patient was given narcotics, place the patient in the supine position. Disinfection with an antiseptic surgical field then narrowed with sterile linen. Prepuce in the wash with antiseptic fluid around the glans penis. Preputium the clamps on the 3 spot. Preputium the scissors on the dorsal side of the penis to the limit glandis corona. Created teugel at the end of the incision. The same Teugel done on frenulum penis. Preputium then cut a circle parallel to the corona glandis. Then the skin and mucosa sutured with plain gut 4.0 atraumatic interupted cut.
complications of surgery
Bleeding, it is currently rare.
Mortality (none)
postoperative care
Post-surgical patients can be directly outpatient, observed the possibility of people with life-threatening complication such as antibiotics and analgesics perdarahan.Pemberian
Friday, August 12, 2011
Guidelines for a Formal Report

Final presentation of the official report consists of three sections: the first round as the accompanying letter, the title page, table of contents and a summary and the body, which includes an introduction, discussion of results and summary of findings and recommendations, and additional components such as the works cited, bibliography and notes .
Letter of transmittal
First impressions are important, as the letter or memo authorizing the report should be seriously considered. The letter must:
Deliver the report ("This is the report requested by ')
An overview of the report
Offer to meet to discuss the contents
Page Title
The first page of a report contains the report title, the name of the recipient or the recipient, the name of the author and the company, date and sometimes a series of reports.
Summary
An abridged version of the entire report, in non-technical, short written and informative, usually describes the salient features of the report draws a core message, and make a recommendation, always written last, after the rest of the report was written.
Table of Contents
Displays the content and layout of the report, always include a list of plants, and sometimes a list of illustrations.
Introduction/Presentation
Prepares the reader for the forthcoming discussion are the purpose and scope of the report and provides background information so that readers can read and intelligent discussion. The introduction should motivate the reader. The reader should understand why the problem has been studied and why the study is a contribution to existing knowledge. Guffey and Nagle (2003) propose the introduction contains seven items:
Letter of transmittal
First impressions are important, as the letter or memo authorizing the report should be seriously considered. The letter must:
Deliver the report ("This is the report requested by ')
An overview of the report
Offer to meet to discuss the contents
Page Title
The first page of a report contains the report title, the name of the recipient or the recipient, the name of the author and the company, date and sometimes a series of reports.
Summary
An abridged version of the entire report, in non-technical, short written and informative, usually describes the salient features of the report draws a core message, and make a recommendation, always written last, after the rest of the report was written.
Table of Contents
Displays the content and layout of the report, always include a list of plants, and sometimes a list of illustrations.
Introduction/Presentation
Prepares the reader for the forthcoming discussion are the purpose and scope of the report and provides background information so that readers can read and intelligent discussion. The introduction should motivate the reader. The reader should understand why the problem has been studied and why the study is a contribution to existing knowledge. Guffey and Nagle (2003) propose the introduction contains seven items:
- Explaining how the report was created and why it is not allowed.
- Description of the problem that the report and asked specific questions to be solved.
The purpose of the report.
Scope (boundaries) and limitations or restrictions on research.
Sources and methods of information gathering.
Summary of results, whether the report is written after the deduction.
To follow from the main sections of the report, provides the consistency and the transition to the reader.
The introductory paragraph is usually followed by a review of the literature, often given the heading "Background". The literature is at least the following objectives in the report:
Sources and methods of information gathering.
Summary of results, whether the report is written after the deduction.
To follow from the main sections of the report, provides the consistency and the transition to the reader.
The introductory paragraph is usually followed by a review of the literature, often given the heading "Background". The literature is at least the following objectives in the report:
- Put research into a historical context to show familiarity with relevant developments.
- Distinguish what has been done, what needs to be done.
- Demonstrates how to use your research is based on previous knowledge by presenting and evaluating what is already known about your research topic.
- A point of reference for the interpretation of your own conclusions. Its report shows how extended your study, revised or improved skills in one area.
The objective of the review of the literature is "the logical continuity between previous and present works" demonstrate (APA, 1994, p. 11).
Discussion of Results/Findings
There to do a story that understand all the details, facts and data through the reader what the author has tried what he or she actually found and what he needed or she thinks, should the following fact.
Official reports often visual aids to highlight, summarize or clarify information. Some general guidelines apply to the use of visual aids: the visual material must have titles and headings, should be visually identified and discussed in the text, they need to be near her are in the text, they should, vertically on the page, and the source credited, if his every country. Use graphics software to create professional-looking graphics.
Conclusions
A summary of the main conclusions or milestones in the discussion, the conclusions are only opinions can never defend the action.
Recommendations
If the discussion and conclusions suggest that certain measures should be taken, the recommendations is to do what categorically.
Discussion of Results/Findings
There to do a story that understand all the details, facts and data through the reader what the author has tried what he or she actually found and what he needed or she thinks, should the following fact.
Official reports often visual aids to highlight, summarize or clarify information. Some general guidelines apply to the use of visual aids: the visual material must have titles and headings, should be visually identified and discussed in the text, they need to be near her are in the text, they should, vertically on the page, and the source credited, if his every country. Use graphics software to create professional-looking graphics.
Conclusions
A summary of the main conclusions or milestones in the discussion, the conclusions are only opinions can never defend the action.
Recommendations
If the discussion and conclusions suggest that certain measures should be taken, the recommendations is to do what categorically.
References
A list of the documents used to complete the project is complete and the author believes will be useful for the reader contains enough information for the reader to correctly identify and order the documents.
At the end of the report, all references are included on a page titled "References", as shown.
Books:
Corporate Author:
Internet
Journals:
Articles
A list of the documents used to complete the project is complete and the author believes will be useful for the reader contains enough information for the reader to correctly identify and order the documents.
At the end of the report, all references are included on a page titled "References", as shown.
Books:
Corporate Author:
Internet
Journals:
Articles
Bibliography
It is recommended that a bibliography listing all sources consulted in the research, whether quoted or not, in fact, be included in an official report.
Attachments
A section at the end of the report that the required data (eg charts, diagrams, photos, technical data and test results), which is deservedly in the discussion, but if it contains trapped with him, and would interfere with the disorder the grand narrative.
10 Principles of Economics
Understanding 10 principles is the key to understanding the whole concept of the economy.
Tradeoffs:
How we make decisions that we make compromises that we have chosen something more something else, or we must give up something else I have. Decisions include how to buy a child a compromise between the money for themselves, money and the child's needs, but also includes trade from the moment you give up your personal information or leisure time for the baby. Shown in giving the film is a very good example of compromise. It shows a college student, to move to Washington if he wants the college has ended, and are part of the time it uses to search for tests or examinations of study for an hour for jobs Washington. The decision on its priorities over others, he faces a compromise. Society as a whole is also disadvantages: The government must decide how to spend a lot of money in some aspects of the country. Something that I personally was happy and made me think when the movie shows how we still have to compromise in the environment: "We all want clean air, but the tradeoff is the loss of income or even the loss of jobs for some Americans "means, says the presenter. I did not understand the relationship between these two until they speak for a coal company in Ohio that had to be closed because he also harmful to the environment, the consequences? Over a thousand people lost their jobs, the Council decided to have a cleaner environment, but the compromise was the loss of jobs of all employees .
Opportunity cost
What do you sacrifice to get something in its economy. The presenter and Gregory Mankiw explains this principle with a college student. To change the election four years of college gives students the costs are many. It is the cost of money in their books and tuition, and also the "opportunity cost", as Mr Mankiw, because they decided to go to college, that 'they provide is the ability to obtain employment and wages are the work would have taken. "Nothing is free, our time is worth something," said Todd Buchholz, an economist, you see that it is a charge of something no longer involved with the money, makes the cost of something, what you can do as much time with your loved ones. This segment of the film contrasts in situations where varying opportunity costs, is shown an example of how the opportunity cost of a student is quite low because that the student abandons low-paid jobs, but the opportunity cost of a very talented high school athletes offered to go directly to Professional is very high, because if they go to college, he gave millions of dollars that he won a professional athlete who decides.
Marginal Thinking
A reasonable person as a student in the film shows, think on, because if too much work to finish college instead of the job that earns money for personal expenses, they simply cut back a bit to work. It is not radical, she is finishing the adjustment, rather, they thought at the edge. Another good example is that of a Broadway that is often met with empty seats. So think on the edge, they decide to negotiate with the public and sell tickets at half price a few hours before the show, the empty spaces in the show. Adjustment of the ticket price the theater actually receives more sales, because even if they deserve 50% of original cost, which is greater than zero, if the seats would have remained empty. By rational thinking and better decisions on the board and make decisions.
Incentives
If the costs and benefits of something different or to change to change our decisions. "When my son, I want to wash my car if my car says you can use it in the evening today is an incentive," said Robert Sobel of Hofstra University and is for me the best explanation of the steps incentives. The incentive is what they say to use the car that night, in other words, it benefits from, yes, but if they do not have all the incentives, it would probably to doubt it. A very good example they set, how we respond to incentives, and refers to the situation today is that how we as a reaction to gas prices. In Europe, the price of gasoline is very high, this incentive makes people buy smaller, more fuel-efficient cars, unlike America, where the price is still relatively low, and people buy big cars and vans. Did you not notice that the shops and streets were the "Tax Free Week" here in Florida packed? This is because people incentives, incentives that will benefit react, apparently you buy more, if you will not be taxed. When President Clinton was in office, he asked the price of cigarettes in the amount of one dollar and a half because it was shown that young people not to smoke and buy cigarettes. This is a perfect example of an obstacle, because it discourages young people from smoking. Another point that explains the behavior of some people taking incentives. Seat belts are now required, as it is effective in saving lives, but instead: "There is evidence that behavior change in response to that seat belts do," says Gregory, because some people exceed the speed limit because they feel safer.
Trade
Since we are not self-sufficient we operate. "People are specialized, people do certain tasks and relying on other people, doing other tasks for them," said Gregory. For example, a hairdresser cut their business services (eg haircuts) for money, and the other person relies on her hairdresser let their hair. "The idea I have something and you have something, and if we change we're both going to be better off is basically what makes the economy," says Caroline Hoxby. We as human beings and be able to survive, we act, we change, we rely on. This is explained in more detail in another example in the film. We leave in a group of dedicated farmers who grow food for us, we both benefit, because we get food, and they are paid for the production of food. Countries to trade between them, if they are good products, cheaper to sell. We work every day to survive.
Markets
Agreements are made on the markets, and prices are installed, which then communicates with the world. In the food market, farmers sell their products and supermarket owners buy and sell. Another type of market is the stamp market. Mark Easter is a stamp dealer explained that as the stock market, where dealers go for the highest price offered. The first person who works as a market, Adam Smith was the grandfather of the economy, says the first book published on the economy called "The Wealth of Nations" in 1776. How can buyers and sellers interact with each other and not create chaos? Adam Smith said, "the markets, as guided by an invisible hand at least a desirable allocation of resources." We all have interests, and if we try everything to achieve this goal, we would all be happy. The invisible hand in the film is a simple example of Mr. Sobel said he said, "If I have a $ 25 dollar and you have a good and you I want to sell it, we need to win both, they wanted the $ 25 dollars more than good, and I am the good of more than $ 25 dollars you want. "The key to the invisible hand are the prices sellers and consumers depend on them. When communism fell in Russia and Eastern Europe, he showed that the free market is the best way to operate, because people know what they want, how you want, how they want the purchase, and etc.
Government
Sometimes the government is committed to developing better results. This occurs when one of two situations occurs. Only when the market outcome is inefficient, and second, if it fails to efficiently distribute income. In many cases, the externality is the cause of the error. "Externalize is when a business or something individual that creates an impact beyond the immediate buyer and seller of the product. Power plants are obviously for the benefit of users and buyers of electricity, but it also has an externality since the smoke they produce damage to the health of a person can. market power can also lead to market failure because a particular company or in-person to control oversize and affect prices. If the market is not fair to the government as well. Some people have their services paid more than the others, is something that can not be controlled by the invisible hand. If the government gets involved, because the situation is very complicated, more complicated, it is, the harder it is for the government to address them.
How we make decisions that we make compromises that we have chosen something more something else, or we must give up something else I have. Decisions include how to buy a child a compromise between the money for themselves, money and the child's needs, but also includes trade from the moment you give up your personal information or leisure time for the baby. Shown in giving the film is a very good example of compromise. It shows a college student, to move to Washington if he wants the college has ended, and are part of the time it uses to search for tests or examinations of study for an hour for jobs Washington. The decision on its priorities over others, he faces a compromise. Society as a whole is also disadvantages: The government must decide how to spend a lot of money in some aspects of the country. Something that I personally was happy and made me think when the movie shows how we still have to compromise in the environment: "We all want clean air, but the tradeoff is the loss of income or even the loss of jobs for some Americans "means, says the presenter. I did not understand the relationship between these two until they speak for a coal company in Ohio that had to be closed because he also harmful to the environment, the consequences? Over a thousand people lost their jobs, the Council decided to have a cleaner environment, but the compromise was the loss of jobs of all employees .
Opportunity cost
What do you sacrifice to get something in its economy. The presenter and Gregory Mankiw explains this principle with a college student. To change the election four years of college gives students the costs are many. It is the cost of money in their books and tuition, and also the "opportunity cost", as Mr Mankiw, because they decided to go to college, that 'they provide is the ability to obtain employment and wages are the work would have taken. "Nothing is free, our time is worth something," said Todd Buchholz, an economist, you see that it is a charge of something no longer involved with the money, makes the cost of something, what you can do as much time with your loved ones. This segment of the film contrasts in situations where varying opportunity costs, is shown an example of how the opportunity cost of a student is quite low because that the student abandons low-paid jobs, but the opportunity cost of a very talented high school athletes offered to go directly to Professional is very high, because if they go to college, he gave millions of dollars that he won a professional athlete who decides.
Marginal Thinking
A reasonable person as a student in the film shows, think on, because if too much work to finish college instead of the job that earns money for personal expenses, they simply cut back a bit to work. It is not radical, she is finishing the adjustment, rather, they thought at the edge. Another good example is that of a Broadway that is often met with empty seats. So think on the edge, they decide to negotiate with the public and sell tickets at half price a few hours before the show, the empty spaces in the show. Adjustment of the ticket price the theater actually receives more sales, because even if they deserve 50% of original cost, which is greater than zero, if the seats would have remained empty. By rational thinking and better decisions on the board and make decisions.
Incentives
If the costs and benefits of something different or to change to change our decisions. "When my son, I want to wash my car if my car says you can use it in the evening today is an incentive," said Robert Sobel of Hofstra University and is for me the best explanation of the steps incentives. The incentive is what they say to use the car that night, in other words, it benefits from, yes, but if they do not have all the incentives, it would probably to doubt it. A very good example they set, how we respond to incentives, and refers to the situation today is that how we as a reaction to gas prices. In Europe, the price of gasoline is very high, this incentive makes people buy smaller, more fuel-efficient cars, unlike America, where the price is still relatively low, and people buy big cars and vans. Did you not notice that the shops and streets were the "Tax Free Week" here in Florida packed? This is because people incentives, incentives that will benefit react, apparently you buy more, if you will not be taxed. When President Clinton was in office, he asked the price of cigarettes in the amount of one dollar and a half because it was shown that young people not to smoke and buy cigarettes. This is a perfect example of an obstacle, because it discourages young people from smoking. Another point that explains the behavior of some people taking incentives. Seat belts are now required, as it is effective in saving lives, but instead: "There is evidence that behavior change in response to that seat belts do," says Gregory, because some people exceed the speed limit because they feel safer.
Trade
Since we are not self-sufficient we operate. "People are specialized, people do certain tasks and relying on other people, doing other tasks for them," said Gregory. For example, a hairdresser cut their business services (eg haircuts) for money, and the other person relies on her hairdresser let their hair. "The idea I have something and you have something, and if we change we're both going to be better off is basically what makes the economy," says Caroline Hoxby. We as human beings and be able to survive, we act, we change, we rely on. This is explained in more detail in another example in the film. We leave in a group of dedicated farmers who grow food for us, we both benefit, because we get food, and they are paid for the production of food. Countries to trade between them, if they are good products, cheaper to sell. We work every day to survive.
Markets
Agreements are made on the markets, and prices are installed, which then communicates with the world. In the food market, farmers sell their products and supermarket owners buy and sell. Another type of market is the stamp market. Mark Easter is a stamp dealer explained that as the stock market, where dealers go for the highest price offered. The first person who works as a market, Adam Smith was the grandfather of the economy, says the first book published on the economy called "The Wealth of Nations" in 1776. How can buyers and sellers interact with each other and not create chaos? Adam Smith said, "the markets, as guided by an invisible hand at least a desirable allocation of resources." We all have interests, and if we try everything to achieve this goal, we would all be happy. The invisible hand in the film is a simple example of Mr. Sobel said he said, "If I have a $ 25 dollar and you have a good and you I want to sell it, we need to win both, they wanted the $ 25 dollars more than good, and I am the good of more than $ 25 dollars you want. "The key to the invisible hand are the prices sellers and consumers depend on them. When communism fell in Russia and Eastern Europe, he showed that the free market is the best way to operate, because people know what they want, how you want, how they want the purchase, and etc.
Government
Sometimes the government is committed to developing better results. This occurs when one of two situations occurs. Only when the market outcome is inefficient, and second, if it fails to efficiently distribute income. In many cases, the externality is the cause of the error. "Externalize is when a business or something individual that creates an impact beyond the immediate buyer and seller of the product. Power plants are obviously for the benefit of users and buyers of electricity, but it also has an externality since the smoke they produce damage to the health of a person can. market power can also lead to market failure because a particular company or in-person to control oversize and affect prices. If the market is not fair to the government as well. Some people have their services paid more than the others, is something that can not be controlled by the invisible hand. If the government gets involved, because the situation is very complicated, more complicated, it is, the harder it is for the government to address them.
Productivity
Statistics show that in 1998 the average American with an annual income of $ 31 500, which had an average of $ 8,300 Mexican and $ 1700 for the average Indian. You may find that their quality of life is not the same as the Americans are better off than the Indians. Productivity explains everything, a rich country produces more poor. And productivity depends on the skills, capital and etc. If a country has an educated workforce, productivity increases. Economic freedom and independence means more productivity. A perfect example is the United States and Hong Kong, where people are free to use their brains to goods, services or ideas that can be taken to the market where consumers benefit from them.
Inflation
This essentially means that inflation, which means that prices are rising all the money that is pressure levels. Printing money is something that must be controlled, because even if it can be "temporarily make people feel richer," as stated by Todd Buchholz increase, possibly based on prices and inflation will come into play, and it is very hard to regain control. Stability between goods and money is the best way to keep inflation at bay.
The Phillips curve
The chairman of the Federal Reserve is to maintain low unemployment and inflation under control. Mr. Mankiw notes that you can not achieve both goals simultaneously and that the policy instrument is the money supply. When one rises the other falls and vice versa, it is called the Phillips curve. As the film explains that it is a compromise in the short term, you must decide on the other. But the compromise does not really exist today, because last year, both inflation and unemployment fell. This does not mean that the Phillips curve would not return in the game, say some economists.
Statistics show that in 1998 the average American with an annual income of $ 31 500, which had an average of $ 8,300 Mexican and $ 1700 for the average Indian. You may find that their quality of life is not the same as the Americans are better off than the Indians. Productivity explains everything, a rich country produces more poor. And productivity depends on the skills, capital and etc. If a country has an educated workforce, productivity increases. Economic freedom and independence means more productivity. A perfect example is the United States and Hong Kong, where people are free to use their brains to goods, services or ideas that can be taken to the market where consumers benefit from them.
Inflation
This essentially means that inflation, which means that prices are rising all the money that is pressure levels. Printing money is something that must be controlled, because even if it can be "temporarily make people feel richer," as stated by Todd Buchholz increase, possibly based on prices and inflation will come into play, and it is very hard to regain control. Stability between goods and money is the best way to keep inflation at bay.
The Phillips curve
The chairman of the Federal Reserve is to maintain low unemployment and inflation under control. Mr. Mankiw notes that you can not achieve both goals simultaneously and that the policy instrument is the money supply. When one rises the other falls and vice versa, it is called the Phillips curve. As the film explains that it is a compromise in the short term, you must decide on the other. But the compromise does not really exist today, because last year, both inflation and unemployment fell. This does not mean that the Phillips curve would not return in the game, say some economists.
Saturday, August 6, 2011
Education outside the classroom
"Education outside the classroom" describes school curriculum learning, other than with a class of students sitting in a room with a teacher and books. It encompasses biology field trips and searching for insects in the school garden, as well as indoor activities like observing stock control in a local shop, or visiting a museum. It is a concept currently enjoying a revival, because of the recognition of benefits from the more active style. The Education and Skills Committee of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom has reported that it brings history and art to life, develops social skills, and clearly enhances geography and science., while DfES has prepared practical guidelines for outdoor activities.
Despite the evidence supporting an extension of outdoor learning for children, there are a number of obstacles in the way. One of these obstacles is risk aversion amongst teachers, parents and others, raising reluctance to such diverse and physical tasks. The journalist Tim Gill has written about parental and institutional risk aversion affecting many activities with children in his book "No Fear". Another obstacle is the perceived high cost of facilitating outdoor learning. Creating an outdoor learning environment needn't cost a great deal, however. The UK Early Years Framework Stage, which outlines best practice in Early Years teaching, asserts that: "Outdoor learning is more effective when adults focus on what children need to be able to do rather than what children need to have. An approach that considers experiences rather than equipment places children at the centre of learning and ensures that individual children's learning and developmental needs are taken account of and met effectively"
Linda Tallent, a UK-based educational consultant who has worked extensively with schools to develop their outdoor spaces into learning environments, agrees. She believes that by focussing on activities and skill development, it is possible to develop an outdoor learning curriculum on a 'shoe string'. She cites a comment by Will Nixon, who reminds readers that 'Using the real world is the way learning has happened for 99.9% of human existence. Only in the last hundred years have we put it into a little box called a classroom.'. Tallent also refers to evidence from a number of studies that the most effective way of learning is through participation, and calls on educators to make a special effort to create opportunities for children to participate in their learning.
Despite the evidence supporting an extension of outdoor learning for children, there are a number of obstacles in the way. One of these obstacles is risk aversion amongst teachers, parents and others, raising reluctance to such diverse and physical tasks. The journalist Tim Gill has written about parental and institutional risk aversion affecting many activities with children in his book "No Fear". Another obstacle is the perceived high cost of facilitating outdoor learning. Creating an outdoor learning environment needn't cost a great deal, however. The UK Early Years Framework Stage, which outlines best practice in Early Years teaching, asserts that: "Outdoor learning is more effective when adults focus on what children need to be able to do rather than what children need to have. An approach that considers experiences rather than equipment places children at the centre of learning and ensures that individual children's learning and developmental needs are taken account of and met effectively"
Linda Tallent, a UK-based educational consultant who has worked extensively with schools to develop their outdoor spaces into learning environments, agrees. She believes that by focussing on activities and skill development, it is possible to develop an outdoor learning curriculum on a 'shoe string'. She cites a comment by Will Nixon, who reminds readers that 'Using the real world is the way learning has happened for 99.9% of human existence. Only in the last hundred years have we put it into a little box called a classroom.'. Tallent also refers to evidence from a number of studies that the most effective way of learning is through participation, and calls on educators to make a special effort to create opportunities for children to participate in their learning.
Outdoor education
Outdoor education usually refers to organized learning that takes place in the outdoors. Outdoor education programs sometimes involve residential or journey-based experiences in which students participate in a variety of adventurous challenges in the form of outdoor activities such as hiking, climbing, canoeing, ropes courses, and group games. Outdoor education draws upon the philosophy, theory, and practices of experiential education and environmental education. 


A group of Outward Bound participants with physical disabilities after completing a ropes course, c. 1996.

An Outward Bound excursion at Lake Superior Provincial Park, Ontario, Canada.
Experiential Education in other countries
The development of Experiential Education in Asian countries
Established in 1973, Breakthrough in Hong Kong was the first non-profit organization that applied the concepts of Experiential Education (though primarily conceptualized in terms of outdoor adventure education) in youth works. Since then, development in Experiential Education has proceeded in Singapore, Taiwan, Macao, and some big cities in mainland China.
Experiential methods in education have existed in China for thousands of years. However, it should be noted that John Dewey was in China in the early 1900s and his ideas were extremely popular. The interest in Dewey's experience in China and contribution are a growing interest.
Established in 1973, Breakthrough in Hong Kong was the first non-profit organization that applied the concepts of Experiential Education (though primarily conceptualized in terms of outdoor adventure education) in youth works. Since then, development in Experiential Education has proceeded in Singapore, Taiwan, Macao, and some big cities in mainland China.
Experiential methods in education have existed in China for thousands of years. However, it should be noted that John Dewey was in China in the early 1900s and his ideas were extremely popular. The interest in Dewey's experience in China and contribution are a growing interest.
Friday, August 5, 2011
MBA Project Reports- Free Downloads

Project Report on Consumer Satisfaction
Download
Download
Mutual Funds Project - Project on Mutual Funds is the better investments plan
Download
PROJECT REPORT OF CUSTOMER FOCUS ON SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Download
Project Report on Study of Conflict Management Strategies
Download
Project Report on Payables Management
Download
Project Report on Effect of Welfare Measures to Employees Morale
Download
PROJECT REPORT ON MARKET SURVEY ON THE BRAND EQUITY
Download
Project Report on Cash management of Standard Charted bank
Download
Project on Post Recession affect on the demand of Nokia E-series
Download
Project Report On Working Capital Analysis
Download
Project on Study of the Customer Relationship Management
Download
Project on Performance Appraisal System
Download
Project report on Equities: Cash & Derivatives
Download
Project Report on Stress Management
Download
Wednesday, August 3, 2011
Accounting period
Accounting period in bookkeeping is the period with reference to which accounting books of any entity are prepared.
It is the period for which books are balanced and the financial statements are prepared. Generally, the accounting period consists of 12 months. However the beginning of the accounting period differs according to the jurisdiction. For example one entity may follow the regular calendar year, i.e. January to December as the accounting year, while another entity may follow April to March as the accounting period.
The International Financial Reporting Standards even allows a period of 52 weeks as an accounting period instead of a proper year.
In some of the ERP tools there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. They put one accounting period as "Year Open" period where all the carried over balances from last financial year are cleared and one period as "Year Close" where all the transactions for closed for the same financial year.
It is the period for which books are balanced and the financial statements are prepared. Generally, the accounting period consists of 12 months. However the beginning of the accounting period differs according to the jurisdiction. For example one entity may follow the regular calendar year, i.e. January to December as the accounting year, while another entity may follow April to March as the accounting period.
The International Financial Reporting Standards even allows a period of 52 weeks as an accounting period instead of a proper year.
In some of the ERP tools there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. They put one accounting period as "Year Open" period where all the carried over balances from last financial year are cleared and one period as "Year Close" where all the transactions for closed for the same financial year.
Accountancy in United States
In the United States, legally practicing accountants are Certified Public Accountants (CPAs), and other non-statutory accountants are Certified Internal Auditors (CIAs), Certified Management Accountants (CMAs) and Accredited Business Accountants (ABAs). The difference between these certifications is primarily the legal status and the types of services provided, although individuals may earn more than one certification. Additionally, much accounting work is performed by uncertified individuals, who may be working under the supervision of a certified accountant. However, as noted above the majority of accountants work in the private sector or may offer their services without the need for certification.
A CPA is licensed by the state of their residence to provide auditing services to the public, although most CPA firms also offer accounting, tax, litigation support, and other financial advisory services. The requirements for receiving the CPA license varies from state to state, although the passage of the Uniform Certified Public Accountant examination is required by all states. This examination is designed and graded by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
A CIA is granted a certificate from the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), provided that the candidate passed a rigorous examination of four parts. A CIA mostly provides their services directly to their employer rather than the public.
A CMA is granted a certificate from the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), provided that the candidate passed a rigorous examination of two parts and meet the practical experience requirement from the IMA. A CMA mostly provides their services directly to their employers rather than the public. A CMA can also provide their services to the public, but to an extent much lesser than that of a CPA.
An ABA is granted accreditation from the Accreditation Council for Accountancy and Taxation (ACAT), provided that the candidate passed the eight-hour Comprehensive Examination for Accreditation in Accounting which tests proficiency in financial accounting, reporting, statement preparation, taxation, business consulting services, business law, and ethics. An ABA specializes in the needs of small-to-mid-size businesses and in financial services to individuals and families. In states where use of the word "accountant” is not permitted by non state licensed individuals, the practitioner may use Accredited Business Adviser.
Public Accountants. In certain states, state law grants State Public Accountant to practice accountancy and taxation (except for audit).
The United States Department of Labor's Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that there are about one million persons employed as accountants and auditors in the U.S.
U.S. tax law grants accountants a limited form of accountant-client privilege.
A CPA is licensed by the state of their residence to provide auditing services to the public, although most CPA firms also offer accounting, tax, litigation support, and other financial advisory services. The requirements for receiving the CPA license varies from state to state, although the passage of the Uniform Certified Public Accountant examination is required by all states. This examination is designed and graded by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
A CIA is granted a certificate from the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), provided that the candidate passed a rigorous examination of four parts. A CIA mostly provides their services directly to their employer rather than the public.
A CMA is granted a certificate from the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), provided that the candidate passed a rigorous examination of two parts and meet the practical experience requirement from the IMA. A CMA mostly provides their services directly to their employers rather than the public. A CMA can also provide their services to the public, but to an extent much lesser than that of a CPA.
An ABA is granted accreditation from the Accreditation Council for Accountancy and Taxation (ACAT), provided that the candidate passed the eight-hour Comprehensive Examination for Accreditation in Accounting which tests proficiency in financial accounting, reporting, statement preparation, taxation, business consulting services, business law, and ethics. An ABA specializes in the needs of small-to-mid-size businesses and in financial services to individuals and families. In states where use of the word "accountant” is not permitted by non state licensed individuals, the practitioner may use Accredited Business Adviser.
Public Accountants. In certain states, state law grants State Public Accountant to practice accountancy and taxation (except for audit).
The United States Department of Labor's Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that there are about one million persons employed as accountants and auditors in the U.S.
U.S. tax law grants accountants a limited form of accountant-client privilege.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)